


I’ve got a complain from the customer of my recent cPanel server installation that his DNS zones are not replicated by our main DNS servers and therefore they have problems.



I’ve got a complain from the customer of my recent cPanel server installation that his DNS zones are not replicated by our main DNS servers and therefore they have problems.
With increasing role of HTTPS websites (Google pushing everybody to run only HTTPS websites considering regular HTTP as insecure) the service provided by Let’s encrypt becomes critically important. But there is a catch – once you get the certificate and redirect your site to HTTPS using .htaccess you will get a problem renewing certificate because 301 redirect breaks the challenge verification and the command
|
1 |
certbot-auto renew |
gives an error about authorization problem.
Read more »


If you are using webmin excellent system for managing virtual host configuration it would make perfect sense to integrate with it the popular certificate authority Letsencrypt that issues completely free SSL certificates.
There are few initial steps that has to be made nside Webmin in order to make it utilize Letsencrypt SSL certificate issuing process for configured virtual hosts. I have successufully configured and used Webmin version 1.831 and certbot-auto 0.12. YMMV.
Read more »
Vmware Workstation is the perfect candidate for configuring local PXE server for testing and development – it contains independent DHCP server that is an equivalent to ISC DHCP v2. All you need is to have your own VM that will be serving as TFTP server for network boot images, there are plenty of instruction on how to do that on Linux (.
I decided to configure my Vmware workstation for windows (windows 7 in that case) DHCP as PXE server using vmNAT network adapter, since I already have Linux VM in vmNAT network which I can configure for TFTP server.
The config file is %SYSTEMDRIVE%\Users\All Users\vmnetdhcp.conf, in order to enable PXE you will need to add 4 lines.
|
1 2 |
allow booting; allow bootp; |
|
1 2 |
next-server <Your-TFTP-VM-IP-Here>; filename "pxelinux.0"; |

Since Letsencrypt started their services life became much easier (or less). You can get free valid and secure SSL certificates that are recognized by majority of browsers, but for that you need to do some initial configuration and keep in mind that if you don’t renew all these nice certificates will turn into pumpkin after 2 month.
Here is the one liner command to install certbot-auto in CentOS 6 (requires additional Python 2.7 from EPEL repo)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
yum -y install python27 python27-devel python27-pip cd /usr/local/sbin wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto chmod +x ./certbot-auto export PYTHON=/usr/bin/python2.7 ./certbot-auto register --agree-tos --no-eff-email -m <your@email.address> |
Almost, the same for the CentOS 7 just without Python.
|
1 2 3 4 |
cd /usr/local/sbin wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto chmod +x ./certbot-auto ./certbot-auto register --agree-tos --no-eff-email -m <your@e-mail.address> |
Here is how quickly request/retrieve certificate for your website on domain.com that is hosted under /home/domain/public_html from command line (presuming that the site is answering on this server already e.g. DNS and web server configured properly)
|
1 2 |
/usr/local/sbin/certbot-auto certonly --webroot \ -w /home/domain/public_html -d domain.com -d www.domain.com |
If the request was successful your new certificates could be accessible from /etc/letsencrypt/live/domain.com, where
privkey.pem – is the certificate key, cert.pem – bare certificate fullchain.pem – certificate along with the whole CA chain.
Don’t forget that these are valid for 2 month only. You’ll need to run
|
1 |
/usr/local/sbin/certbot-auto renew |
after that to get valid certificates.
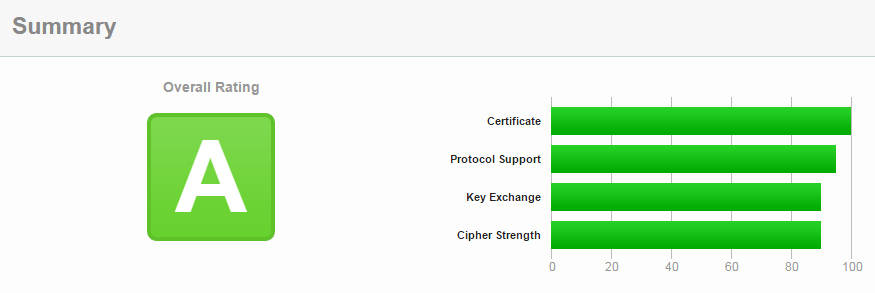
The fine tuning of the SSL server side configuration is slow and tedious but necessary procedure. It’s always good to have your SSL site to conform the most latest security standards. It boosts ego and makes customer happy too. It turns out that all you need for that is already at your disposal the point is to properly configure it.
Read more »
I wrote before about excellent tool BFD that allows to block brute force password guessing attempts on different network services.
I prefer it to Fail2ban because of portability (bash script) system resource consumption (bash script!) and extendаbility (true “unix way” modularity).
I also wrote before a brief instruction on how to extend BFD with your own rule to fight with apache/Wordpress DOS attack.
In this post I will show you how to write custom rules to block SMTP password guessing brute force attempts and SSSHD
I had an interesting complain the other day – customer experienced connectivity problems trying to access some web sites while on PPTP VPN connection. The VPN server was running on Linux and also under our control so troubleshooting the situation was pretty easy. All MS Windows based clients didn’t have this problem, only OSX based clients.
Read more »
Most of modern Linux distributions contain Apache 2.x web server with the set of standard modules. One of these modules is mod_expires that allows to configure content expiration in local browser cache or caching proxies. Proper configuration for it can significantly improve overall server performance and reduce bandwidth consumption.
Read more »
![]() “Extremely friendly…widely used …de-facto industry standard” cPanel all this and more. And I dislike it as much as it popular (I’ll talk about it later).
“Extremely friendly…widely used …de-facto industry standard” cPanel all this and more. And I dislike it as much as it popular (I’ll talk about it later).
What surprised me that cpanel.net web site does not contain the link to the installation instruction on it’s front page which should be only logical.
Read more »